 歡迎來到北京博奧森生物技術有限公司網站!
歡迎來到北京博奧森生物技術有限公司網站! 歡迎來到北京博奧森生物技術有限公司網站!
歡迎來到北京博奧森生物技術有限公司網站!

截至目前,引用Bioss產品發(fā)表的文獻共18150篇,總影響因子78229.601分,發(fā)表在Nature/Science/Cell/Immunity等期刊的文獻共52篇,合作單位覆蓋了清華、北大、復旦、華盛頓大學、麻省理工學院、東京大學以及紐約大學等國際研究機構上百所。
近期收錄2022年4月引用 Bioss 產品發(fā)表的文獻共200篇(圖一),文章影響因子總和高達1110.664分,其中10分以上文獻有13篇,20分以上文獻有2篇(圖二)。
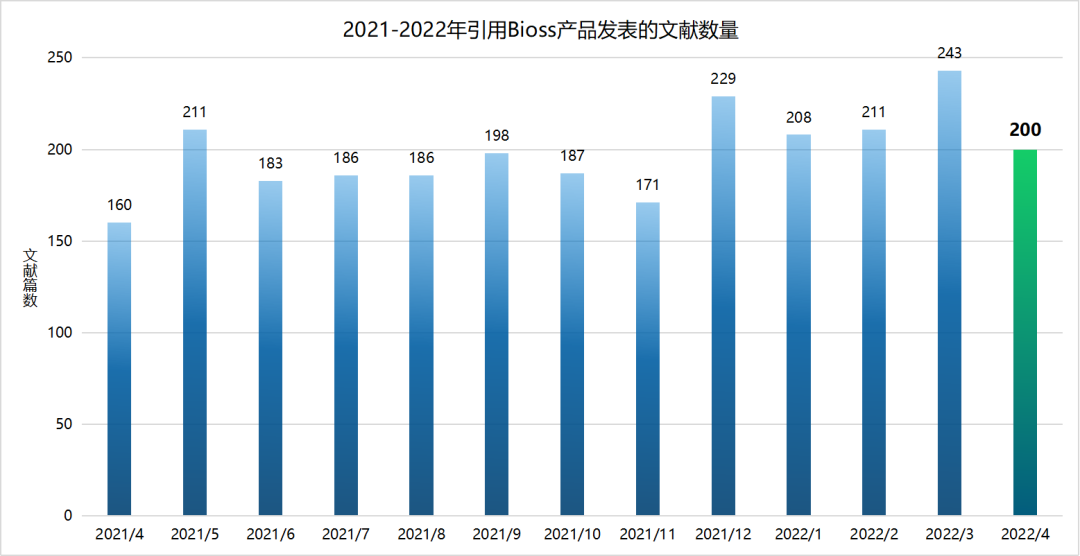
圖一

圖二
Cell Metabolism [IF=27.287]

bsm-0978M (Anti-GAPDH mAb; WB)
摘要:Emerging evidence indicates that the accretion of senescent cells is linked to metabolic disorders. However, the underlying mechanisms and metabolic consequences of cellular senescence in obesity remain obscure. In this study, we found that obese adipocytes are senescence-susceptible cells accompanied with genome instability. Additionally, we discovered that SREBP1c may play a key role in genome stability and senescence in adipocytes by modulating DNA-damage responses. Unexpectedly, SREBP1c interacted with PARP1 and potentiated PARP1 activity during DNA repair, independent of its canonical lipogenic function. The genetic depletion of SREBP1c accelerated adipocyte senescence, leading to immune cell recruitment into obese adipose tissue. These deleterious effects provoked unhealthy adipose tissue remodeling and insulin resistance in obesity. In contrast, the elimination of senescent adipocytes alleviated adipose tissue inflammation and improved insulin resistance. These findings revealed distinctive roles of SREBP1c-PARP1 axis in the regulation of adipocyte senescence and will help decipher the metabolic significance of senescence in obesity.
Autophagy [IF=16.016]

文獻引用抗體:
bs-1353R (Anti-BECN1 pAb; IF)
bs-0295D-AF555 (Donkey Anti-rabbit IgG H&L/AF555; IF)
bs-0296R-AF488 (Rabbit Anti-Mouse IgG H&L/AF488; IF)
摘要:Macroautophagy/autophagy is a cellular and energy homeostatic mechanism that contributes to maintain the number of primordial follicles, germ cell survival, and anti-ovarian aging. However, it remains unknown whether autophagy in granulosa cells affects oocyte maturation. Here, we show a clear tendency of reduced autophagy level in human granulosa cells from women of advanced maternal age, implying a potential negative correlation between autophagy levels and oocyte quality. We therefore established a co-culture system and show that either pharmacological inhibition or genetic ablation of autophagy in granulosa cells negatively affect oocyte quality and fertilization ability. Moreover, our metabolomics analysis indicates that the adverse impact of autophagy impairment on oocyte quality is mediated by downregulated citrate levels, while exogenous supplementation of citrate can significantly restore the oocyte maturation. Mechanistically, we found that ACLY (ATP citrate lyase), which is a crucial enzyme catalyzing the cleavage of citrate, was preferentially associated with K63-linked ubiquitin chains and recognized by the autophagy receptor protein SQSTM1/p62 for selective autophagic degradation. In human follicles, the autophagy level in granulosa cells was downregulated with maternal aging, accompanied by decreased citrate in the follicular fluid, implying a potential correlation between citrate metabolism and oocyte quality. We also show that elevated citrate levels in porcine follicular fluid promote oocyte maturation. Collectively, our data reveal that autophagy in granulosa cells is a beneficial mechanism to maintain a certain degree of citrate by selectively targeting ACLY during oocyte maturation.
JCI【IF=14.808】

文獻引用抗體:
作者單位:日本愛媛大學高級研究支持中心實驗動物研究部
摘要:Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is characterized by chronic synovial inflammation with aberrant epigenetic alterations, eventually leading to joint destruction. However, the epigenetic regulatory mechanisms underlying RA pathogenesis remain largely unknown. Here we showed that Ubiquitin-like containing PHD and RING finger domains 1 (UHRF1) is a central epigenetic regulator that suppressively orchestrates multiple pathogeneses in RA. UHRF1 expression was remarkably up-regulated in synovial fibroblasts (SF) from arthritis model mice and RA patients. Mice with SF-specific Uhrf1 conditional knockout showed more severe arthritic phenotypes than littermate control. Uhrf1-deficient SF also exhibited enhanced apoptosis resistance and up-regulated expression of several cytokines including Ccl20. In RA patients, DAS28, CRP, and Th17 accumulation as well as apoptosis resistance were negatively correlated with UHRF1 expression in synovium. Finally, Ryuvidine administration that stabilizes UHRF1 ameliorated arthritis pathogeneses in a mouse model of RA. This study demonstrated that UHRF1 expressed in RA SF can contribute to negative feedback mechanisms that suppress multiple pathogenic events in arthritis, suggesting that targeting UHRF1 could be one of the therapeutic strategies for RA.
CEJ【IF=13.273】

bs-6194R (Anti-Sclerostin pAb; Other)
摘要:Biomaterial-based tissue engineering has emerged as a hotspot in the field of osteanagenesis. Due to invasive operation in the transplantation process always bring irreparable damage to patients, approaches that enable innate repair mechanisms hold considerable promise for bone repair. To this end, a rational design based on in situ recruitment of stem cells is proposed to circumvent the troublesome problem. In this study, an interpenetration network hydrogel is developed utilizing chitosan (CS), in which the enriched bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs) can undergo a tridimensional and freely proliferation. Moreover, the encapsulation of biological growth factor Wnt3a promotes the differentiation of osteoprogenitor cells with an asymmetric cell divisions (ACD) manner, thereby accelerating bone formation. With this “smart biomaterials”, a robust instant stem cell ingrowth within the deformable hydrogel and a high efficiency of bone regeneration on a murine skull are observed, both of which are vital for clinical applications. Such an osteoinductive system represents the advanced design concept to repair bone defects effectively, and offers a promising strategy for the development of future bone tissue engineering.
JPR【IF=13.007】

bs-0027R (Anti-MT1 pAb; WB, IHC)
摘要:Central serous chorioretinopathy (CSC) is a vision-threatening disease with no validated treatment and unclear pathogenesis. It is characterized by dilation and leakage of choroidal vasculature, resulting in the accumulation of subretinal fluid, and serous detachment of the neurosensory retina. Numerous studies have demonstrated that melatonin had multiple protective effects against endothelial dysfunction, vascular inflammation, and blood–retinal barrier (BRB) breakdown. However, the effect of melatonin on CSC, and its exact pathogenesis, is not well understood thus far. In this study, an experimental model was established by intravitreal injection of aldosterone in rats, which mimicked the features of CSC. Our results found that melatonin administration in advance significantly inhibited aldosterone-induced choroidal thickening and vasodilation by reducing the expression of calcium-activated potassium channel KCa2.3, and attenuated tortuosity of choroid vessels. Moreover, melatonin protected the BRB integrity and prevented the decrease in tight junction protein (ZO-1, occludin, and claudin-1) levels in the rat model induced by aldosterone. Additionally, the data also showed that intraperitoneal injection of melatonin in advance inhibited aldosterone-induced macrophage/microglia infiltration, and remarkably diminished the levels of inflammatory cytokines (interleukin-6 [IL-6], IL-1β, and cyclooxygenase-2), chemokines (chemokine C–C motif ligand 3, and C–X–C motif ligand 1), and matrix metalloproteinases (MMP-2 and MMP-9). Luzindole, as the nonselective MT1 and MT2 antagonist, and 4-phenyl-2-propionamidotetraline, as the selective MT2 antagonist, neutralized the melatonin-induced inhibition of choroidal thickening and choroidal vasodilation, indicating that melatonin might exert the effects via binding to its receptors. Furthermore, the IL-17A/nuclear factor-κB signaling pathway was activated by intravitreal administration of aldosterone, while it was suppressed in melatonin-treated in advance rat eyes. This study indicates that melatonin could serve as a promising safe therapeutic strategy for CSC patients.
APSB【IF=11.413】

文獻引用抗體:
作者單位:武漢大學基礎醫(yī)學學院藥理學系
※ 點擊這里查看往期單月Bioss抗體產品文獻引用列表